Over the years, manufacturing technology has evolved with more advanced features and functionality. To date, 3D printing and injection moulding are some of the most commonly used manufacturing techniques. Both methods are used for prototyping and custom parts. In this article, we explore the differences and similarities between 3D printing and injection moulding to help you choose the best option for your project.
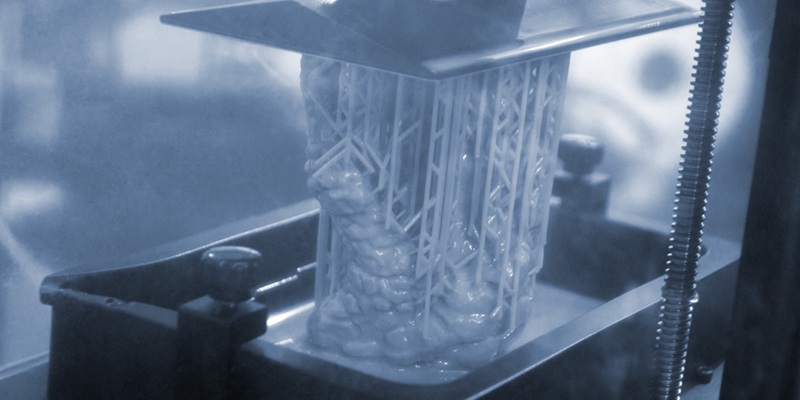

What Is 3D Printing?
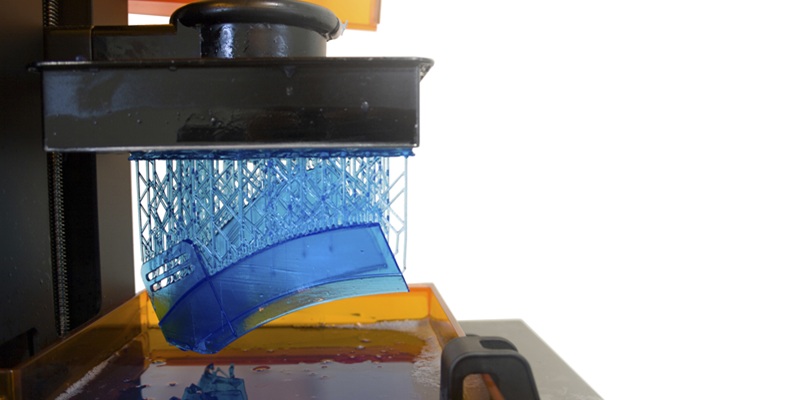
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process where parts are created layer by layer from digital 3D models. This technology has evolved significantly over the years, and today, advanced industrial 3D printing methods are used to meet the demands of professional applications.
Technologies like SLA (Stereolithography) and SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) are now widely adopted in many industries due to their ability to handle larger machine sizes and more complex processes, enabling the production of high-precision, durable parts for various industries.
Advantages Of 3D Printing
Here are the advantages of 3D printing:
- Customizable: It’s easy to perform design changes during production to save time and cost, as it can be paused mid-process
- Low initial investment: No costly tooling, and the equipment and materials are generally more affordable compared to traditional manufacturing setups.
- Design flexibility: 3D printing produces the parts layer by layer, which is perfect for unique or complex designs
- Rapid prototyping: The turnaround time can be as quick as a few hours, suitable for fast production
Limitations Of 3D Printing
Take a look at the disadvantages of 3D printing below:
- Not suitable for high-scale production: There are limitations as it has longer cycle times and can’t meet large-sized parts
- Uneven surface: The surface finish is rough and requires post-finishing to smooth it afterwards
- Limited thermal and mechanical properties: Not all 3D printed materials match high strength, heat resistance, or chemical resistance molded or machines materials
- Slower production speeds: Compared to molding, 3D printing takes longer to produce large quantities, making it better suited for small batches or prototypes.

What Is Injection Moulding?
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts involving melting thermoplastic material and injecting it into a mould cavity under high pressure. The mould is put under pressure to ensure the melted material fills the entire mould. As the plastic cools, it solidifies into the intended shape. Once hardened, the finished part is removed from the mould and is ready for use.
Advantages Of Injection Moulding
Here are some of the advantages of injection moulding:
- Efficient for low volume production: Able to produce parts for small batches of parts with consistent quality and minimal defects and differences
- Cost-effective: The cost per part is considered to be low compared to other manufacturing methods
- Fast cycle times: The mould cycle takes just a few minutes, which produces faster turnaround times
Limitations Of Injection Moulding
Let’s take a look at the disadvantages of injection moulding:
- Design inflexibility: Frequent design changes can be costly and time-consuming once the mould is created
- High upfront costs: The initial investment will be high as the tools are expensive
- Longer lead times for tooling: It typically takes several weeks to create the mould, which extends the overall production timeline
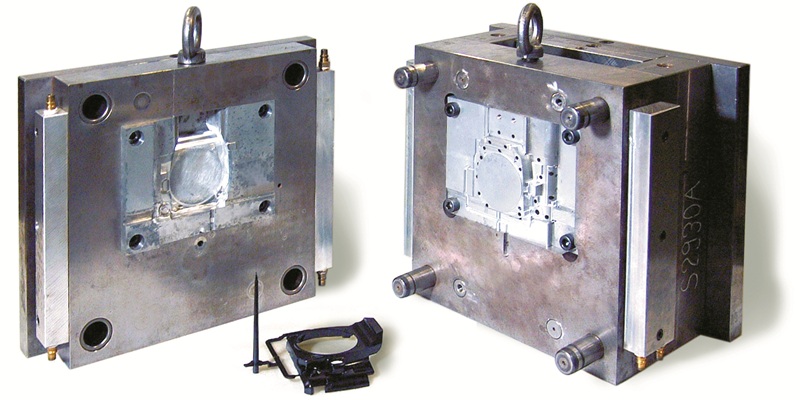
3D Printing Vs Injection Moulding: What Are The Key Differences?
Here’s a breakdown of the key differences between 3D printing and injection moulding:
| 3D Printing | Injection Moulding | |
| Setup Cost | Minimal setup, aside from print preparation and post-processing | High set up cost due to mould fabrication and machine configuration |
| Cycle Times | Slower cycle times, as it depends on part complexity and size | Fast cycle times once the mould is created |
| Lead Times | Short lead time (hours to a few days), ideal for rapid prototyping | Longer lead time (mould creation can take weeks) |
| Complexity of Design | Supports flexible, complex designs and is easy to amend | Limited design complexity unless multiple molds are used, and design changes are time-consuming |
| Strength | Less strong and rigid (material-dependent) | Generally, more durable and rigid parts |
Let’s find out the key differences between 3D printing and injection moulding in more detail below:
1. Costs
The upfront costs of 3D printing are relatively low due to minimal setup and does not require expensive tooling, and setup is minimal aside from print preparation and post-processing.
In contrast, injection moulding has high initial costs due to the need for custom tooling and equipment.
2. Cycle Times
Cycle times for 3D printing are generally slower, depending on the complexity and size of the parts. In contrast, injection moulding offers much faster cycle times, allowing parts to be produced quickly once the mould is created.
3. Lead Times
The lead time for 3D printing can be a few hours up to a few days. This means it can rapidly produce prototypes easily. But for injection moulding, the mould creation may take time, up to a few weeks.
4. Complexity of Design
The design for 3D printing can be flexible and complex. It can also be easily amended and revised accordingly without being too time-consuming. Injection moulding may not allow for too complex designs because it uses the same mould, but it may be possible if multiple moulds are used. However, amendments to the design are not recommended, as they will extend the production time.
5. Strength
In terms of strength, 3D printed parts are typically less strong and rigid than those made through injection moulding, although material choice plays a significant role. Injection moulded parts are generally more durable and better suited for end-use applications.
3D Printing Vs Injection Moulding: What Are The Similarities?
In terms of similarities, let’s take a look at the key points below:
- Materials: Both methods can utilize a range of materials, including plastics, metals, and composites, though the material properties may vary depending on the specific technology.
- Applications: Both industrial 3D printing and injection moulding are used across a wide range of industries, producing parts such as automotive components, medical device housings, consumer electronics casings, and industrial equipment parts.
- Complexity: Both methods support a range of design possibilities, but 3D printing offers greater flexibility for making design changes during production, whereas implementing design modifications in injection moulding can be time-consuming and costly
Create Your Products With ARRK Asia
Both manufacturing methods have their own advantages and disadvantages, depending on the purpose and industry. When comparing 3D printing and injection moulding, the best way to know the best option would be to identify your requirements and needs.
ARRK Asia consists of a team of professionals who are more than capable of assisting you to choose the most suitable manufacturing method for your project. Contact us today to let us bring your ideas to life.